TypeScript SDK
The cloud notification service enables server-side applications to send interactive notifications with support for hierarchical organizational structures, flexible targeting options, and cross-platform delivery. The service communicates with your server-side applications via the TypeScript SDK or the Java SDK.
For an overview, see HERE cloud notification service overview
Installation
- Install the latest version of Node.js on your server: https://nodejs.org/en/download
If you need to maintain multiple versions of Node, you can use nvm to install Node.
- Use npm (comes with Node) or yarn to install the
@openfin/cloud-notification-core-apipackage.
npm install @openfin/cloud-notification-core-api
yarn add @openfin/cloud-notification-core-api
Basic setup
To get started, you'll need to import the CloudNotificationAPI class and configure your connection settings.
The basic setup requires a platform ID and authentication method.
// Import the main CloudNotificationAPI class
import {CloudNotificationAPI} from "@openfin/cloud-notification-core-api";
// Configure connection settings
const connectSettings = {
platformId: PLATFORM_ID, // Unique identifier for your platform
authenticationType: "basic", // Authentication method (basic, oauth, default)
logger: (level, message) => { // Optional: Custom logging function
console.log(`\nAPI Log [${level}] ${message}\n`);
},
};
// Create a new notification API instance
const notificationApi = new CloudNotificationAPI({
url: "https://<env>/notifications", // Your notification server endpoint
});
Establish a connection
Once you've configured your settings, you need to establish a connection to the notification service. This creates an authenticated connection that's used for all subsequent operations.
let connectionResult;
try {
// Attempt to establish connection to the notification service
connectionResult = await notificationApi.connect(connectSettings);
console.log("Connected successfully");
} catch (error) {
// Handle connection failures gracefully
console.error("Connection failed: ", error);
process.exit(1); // Exit if we can't connect
}
Event listeners
Set up event listeners to handle connection state changes and incoming notifications. These listeners ensure your application responds appropriately to network issues, connection expiration, and new messages.
// Handle automatic reconnection after network issues
notificationApi.addEventListener("reconnected", () => {
console.log("Connection Reconnected");
});
// Handle unexpected disconnections
notificationApi.addEventListener("disconnected", () => {
console.log("Connection Disconnected");
process.exit(1); // Exit application on disconnect
});
// Handle incoming notifications from other clients
notificationApi.addEventListener("notification", (event) => {
console.log("Notification Received");
// Unique notification identifier
console.log(`ID: ${event.notificationId}`);
// Your custom correlation ID
console.log(`Correlation ID: ${event.correlationId}`);
// Who the notification was sent to
console.log(`Target: ${event.target}`);
// Type of action (create, update, etc.)
console.log(`Action: ${event.action}`);
// The actual notification content
console.log(`Payload:`, event.payload);
});
Publish notifications
Once connected, you can send notifications to users and groups. Notifications can be simple text messages or complex content with markdown formatting, images, and interactive elements.
Notification payloads in the cloud service are structured in the same way as notification objects in Notification Center.
Basic notification
Here's how to send a simple notification with text content and basic targeting.
correlationId is an optional, user-defined ID that correlates a notification with the users' custom data.
const result = await notificationApi.raiseNotification(
// Targeting configuration
{
// Your custom ID for tracking this notification
correlationId: CORRELATION_ID,
targets: {
// Send to users in the "london" group
groups: [GROUP_NAME],
// Also send to specific users
users: [USER_EMAIL],
},
},
// Notification content and styling
{
// Support for markdown formatting
template: "markdown",
// Visual indicator (info, warning, error, etc.)
indicator: { type: "info" },
// Notification title
title: "Important Update",
// Main content
body: "This is a notification with **markdown** support!",
// Category for organization/filtering
category: "Updates",
// Path to notification icon
icon: "ui/icon.png",
// Your custom data for the application
customData: { context: "example" },
// Action to perform when user clicks
onSelect: { task: "ViewDetails" },
// Timestamp for the notification
date: new Date(),
// Display behavior (sticky, temporary, etc.)
toast: "sticky"
}
);
// Returns notification ID and status
console.log("Notification sent:", result);
Group targeting and hierarchies
Target notifications using hierarchical group structures for efficient and flexible notification distribution.
The service supports hierarchical group targeting. For example, given this group structure:
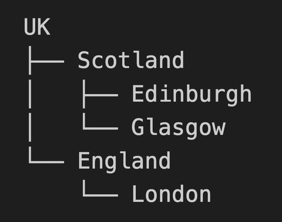
- Targeting London sends to direct London group members only
- Targeting Scotland sends to Scotland, Edinburgh, and Glasgow members
- Targeting UK sends to all members in the hierarchy
In the case of duplication, all members receive only one notification.
// Target specific group only - no inheritance
const londonOnly = {
targets: {
// Only direct members of London group receive the notification
groups: ["London"],
users: []
}
};
// Target group and all subgroups - inheritance applies
const scotlandAll = {
targets: {
// Scotland, Edinburgh, and Glasgow members all receive it
groups: ["Scotland"],
users: []
}
};
// Target entire hierarchy - maximum reach
const ukAll = {
targets: {
// All UK members and subgroups receive the notification
groups: ["UK"],
users: []
}
};
// Mixed targeting - combine groups and individual users
const mixed = {
targets: {
// Multiple groups
groups: ["London", "Edinburgh"],
// Plus specific individuals
users: [USER_EMAIL]
}
};